Edge Computing: Bringing Intelligence Closer to the Source
Related Articles: Edge Computing: Bringing Intelligence Closer to the Source
- Quantum Computing
- Brain-Computer Interface (BCI)
- Blockchain For Security
- OLED Vs. AMOLED Displays
- Eco-friendly tech gadgets 2025
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Edge Computing: Bringing Intelligence Closer to the Source. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Video about Edge Computing: Bringing Intelligence Closer to the Source
Edge Computing: Bringing Intelligence Closer to the Source
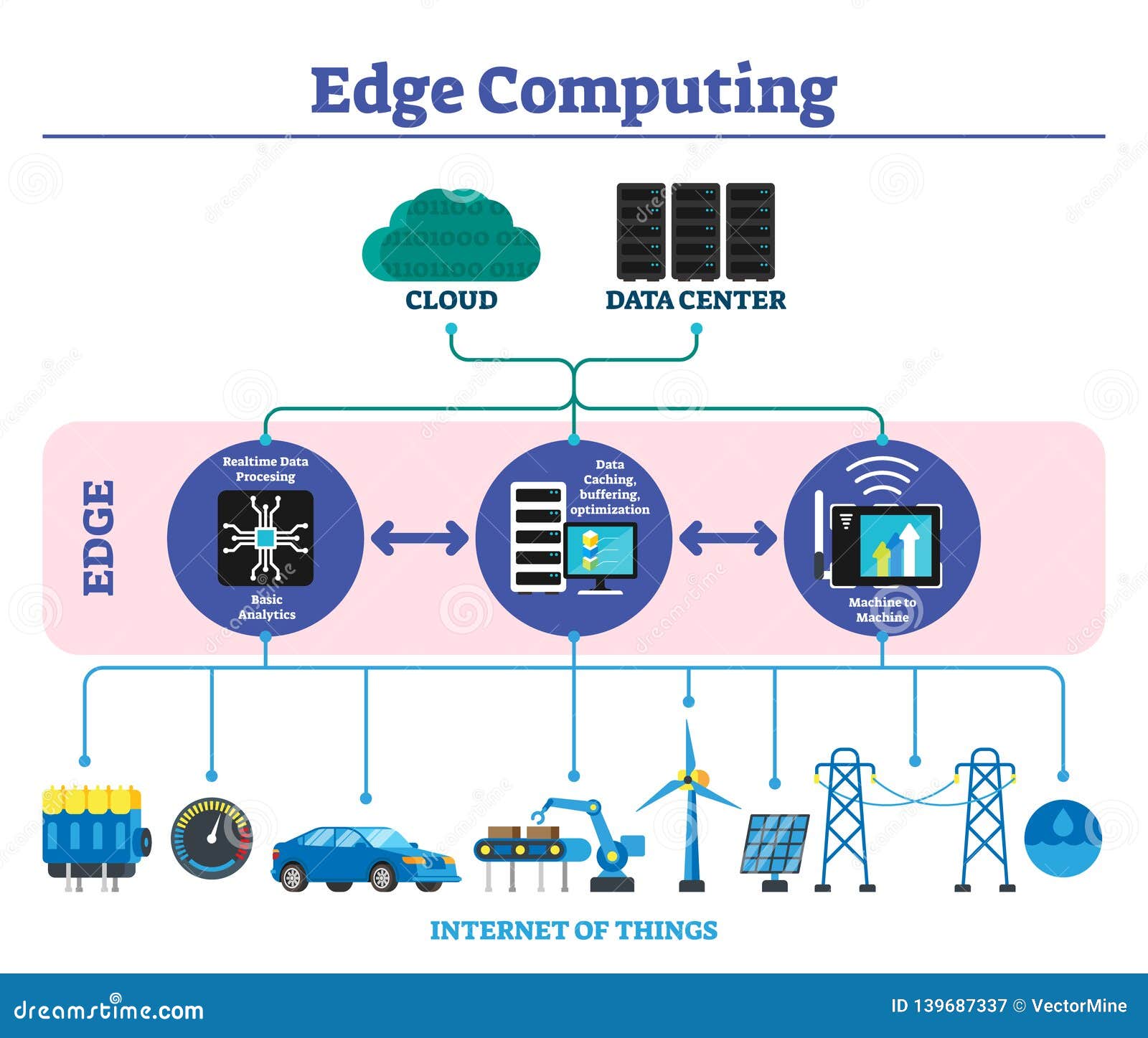
The digital revolution has ushered in an era of unprecedented data generation. From connected cars and smart homes to industrial sensors and wearable devices, the volume of data being produced is growing exponentially. This data deluge, while offering immense potential, presents significant challenges for traditional cloud-centric architectures. Enter edge computing, a paradigm shift that’s bringing processing power closer to the source of data, transforming how we collect, process, and analyze information.
Understanding the Edge
Edge computing is a decentralized computing approach where data processing and application execution occur closer to the data source, rather than relying solely on centralized cloud servers. This "edge" can be anywhere from a local server in a building to a small device embedded within a machine. The key is reducing the distance data travels before being processed, thereby minimizing latency and bandwidth consumption.
Unlike cloud computing, which relies on massive data centers often located far from the point of data generation, edge computing pushes processing power and storage resources to the edge of the network. This strategic distribution offers a range of advantages that are reshaping industries across the board.
The Benefits of Edge Computing
The benefits of adopting edge computing are compelling and far-reaching. Here are some key advantages:
-
Reduced Latency: This is arguably the most significant advantage. By processing data locally, edge computing dramatically reduces the time it takes to analyze and respond to information. This is crucial for applications requiring real-time responses, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and augmented reality. The milliseconds saved can be the difference between success and failure in many critical applications.
-
Improved Bandwidth Efficiency: Sending massive amounts of raw data across long distances consumes significant bandwidth. Edge computing minimizes this by processing data locally, only transmitting processed or aggregated data to the cloud. This reduces network congestion and associated costs.
-
Enhanced Security: Keeping sensitive data close to its source can enhance security. Less data needs to be transmitted across potentially vulnerable networks, reducing the risk of data breaches and cyberattacks. This is particularly important in industries with stringent security requirements, such as healthcare and finance.

-
Increased Reliability: Edge computing provides resilience against network outages. If the connection to the cloud is lost, edge devices can continue operating locally, ensuring uninterrupted service. This is critical for applications where continuous operation is essential, such as industrial control systems and emergency response systems.

Support for Real-time Analytics: The low latency inherent in edge computing enables real-time data analysis. This allows for immediate insights and faster decision-making, empowering businesses to react quickly to changing conditions and optimize their operations.
-
Cost Savings: While the initial investment in edge infrastructure can be significant, the long-term cost savings can be substantial. Reduced bandwidth consumption, improved efficiency, and minimized downtime contribute to significant cost reductions over time.
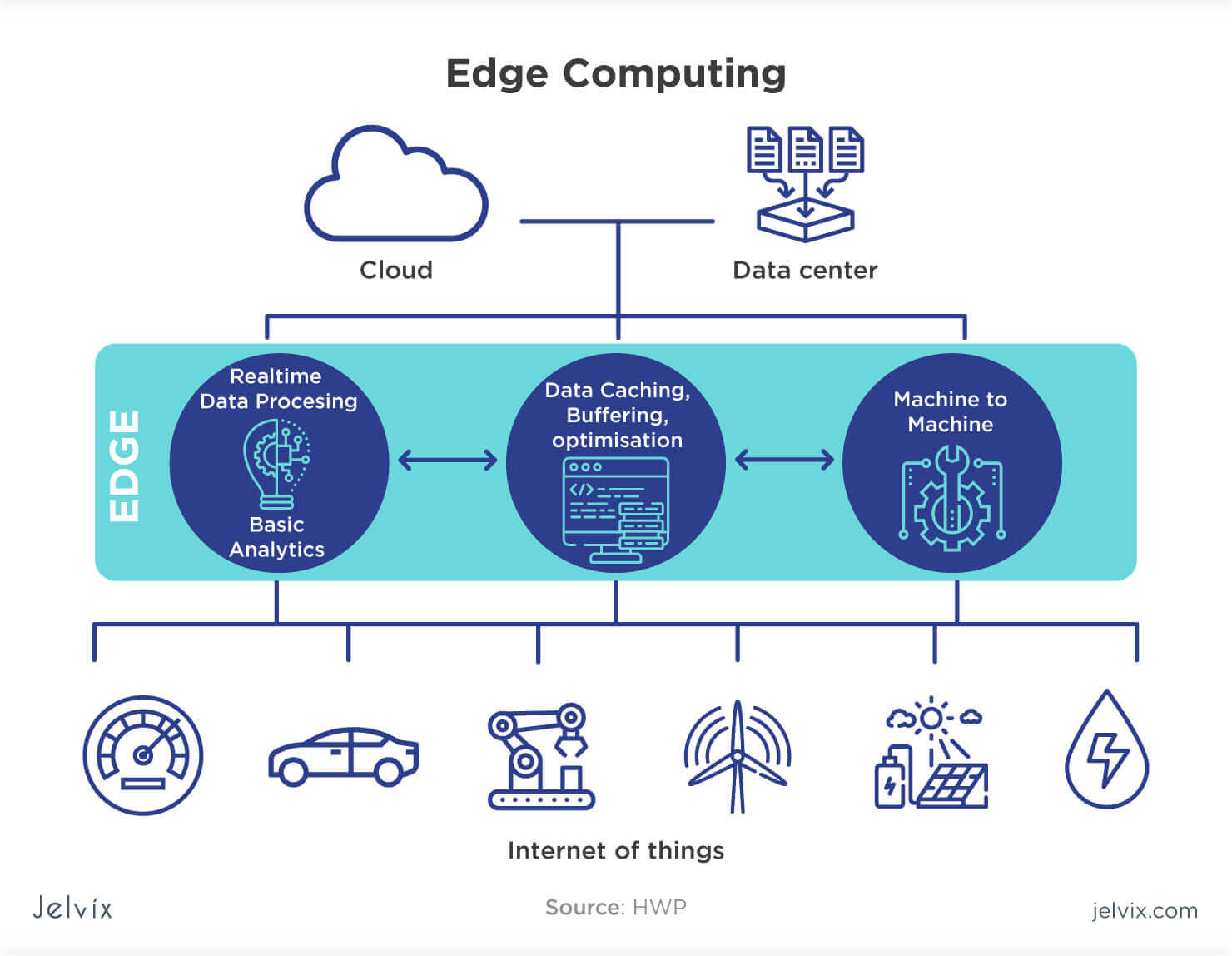
Applications of Edge Computing
Edge computing is rapidly transforming various industries. Here are some notable examples:
-
Manufacturing: Edge computing empowers smart factories with real-time monitoring of equipment, predictive maintenance, and optimized production processes. Sensors embedded in machinery collect vast amounts of data, which is processed at the edge to identify potential problems before they occur, preventing costly downtime.
-
Healthcare: In healthcare, edge computing is revolutionizing patient care. Wearable sensors monitor vital signs and transmit data to edge devices for real-time analysis, enabling early detection of health issues and immediate interventions. This is particularly beneficial for remote patient monitoring and emergency response systems.
-
Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars rely heavily on edge computing to process sensor data in real-time, enabling them to navigate safely and efficiently. The low latency of edge processing is crucial for quick reactions to changing road conditions and avoiding accidents.
-
Smart Cities: Edge computing plays a vital role in building smart cities. It enables real-time traffic management, optimized energy consumption, and improved public safety through the integration of various sensors and devices.
-
Retail: In retail, edge computing enhances customer experiences through personalized recommendations, improved inventory management, and real-time fraud detection. It also enables efficient operations by optimizing supply chains and streamlining logistics.
-
Oil and Gas: In the oil and gas industry, edge computing improves safety and efficiency by monitoring remote assets, optimizing drilling operations, and reducing environmental impact. The ability to process data locally is crucial in remote and challenging environments.
Challenges of Edge Computing
Despite its numerous advantages, edge computing faces several challenges:
-
Security Concerns: While edge computing enhances security in some aspects, it also introduces new security challenges. Securing numerous edge devices and ensuring data integrity across a distributed network requires robust security measures.
-
Management Complexity: Managing a large number of distributed edge devices can be complex. Effective monitoring, maintenance, and updates require sophisticated management tools and strategies.
-
Data Integration and Standardization: Integrating data from various edge devices and ensuring data consistency can be challenging. The lack of standardization across edge devices and platforms makes interoperability a concern.
-
Power Consumption: Edge devices, especially those deployed in remote locations, may have limited power sources. Optimizing power consumption is crucial for ensuring the longevity and sustainability of edge deployments.
-
Cost of Deployment: The initial investment in edge infrastructure can be substantial, especially for large-scale deployments. Careful planning and cost optimization are essential for maximizing return on investment.
The Future of Edge Computing
The future of edge computing is bright. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more widespread adoption across various industries. The convergence of edge computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT) is poised to unlock unprecedented opportunities for innovation and efficiency. We can anticipate:
-
Increased sophistication in AI at the edge: More powerful edge devices will enable more complex AI algorithms to be executed locally, leading to faster and more accurate insights.
-
Greater interoperability and standardization: The development of open standards and interoperable platforms will simplify the deployment and management of edge systems.
-
Improved security and privacy measures: Advances in cybersecurity technologies will enhance the security and privacy of edge deployments.
-
Enhanced integration with cloud computing: Hybrid cloud-edge architectures will combine the strengths of both cloud and edge computing, creating a more robust and flexible computing infrastructure.
-
Wider adoption in emerging technologies: Edge computing will play a critical role in the development and deployment of emerging technologies such as augmented reality, virtual reality, and the metaverse.
In conclusion, edge computing is not merely a technological advancement; it’s a paradigm shift that’s fundamentally changing how we interact with data and technology. By bringing intelligence closer to the source, it unlocks opportunities for enhanced efficiency, improved security, and faster decision-making across a wide range of industries. While challenges remain, the benefits are undeniable, and the future of edge computing is poised for continued growth and innovation.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Edge Computing: Bringing Intelligence Closer to the Source. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!