Blockchain: The Revolutionary Technology Reshaping Industries
Related Articles: Blockchain: The Revolutionary Technology Reshaping Industries
- Best apps for productivity in 2025
- Top artificial intelligence courses
- AI tools for digital marketing
- Smartphone Virtual Reality Headsets
- Neural Processing Units (NPUs)
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Blockchain: The Revolutionary Technology Reshaping Industries. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Video about Blockchain: The Revolutionary Technology Reshaping Industries
Blockchain: The Revolutionary Technology Reshaping Industries

The digital revolution has ushered in an era of unprecedented technological advancements, and among the most transformative is blockchain technology. Initially conceived as the underlying technology for the cryptocurrency Bitcoin, blockchain has rapidly evolved beyond its nascent applications, demonstrating its potential to revolutionize diverse industries and reshape our digital landscape. This article delves into the intricacies of blockchain, exploring its core principles, applications, advantages, challenges, and future prospects.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Blockchain
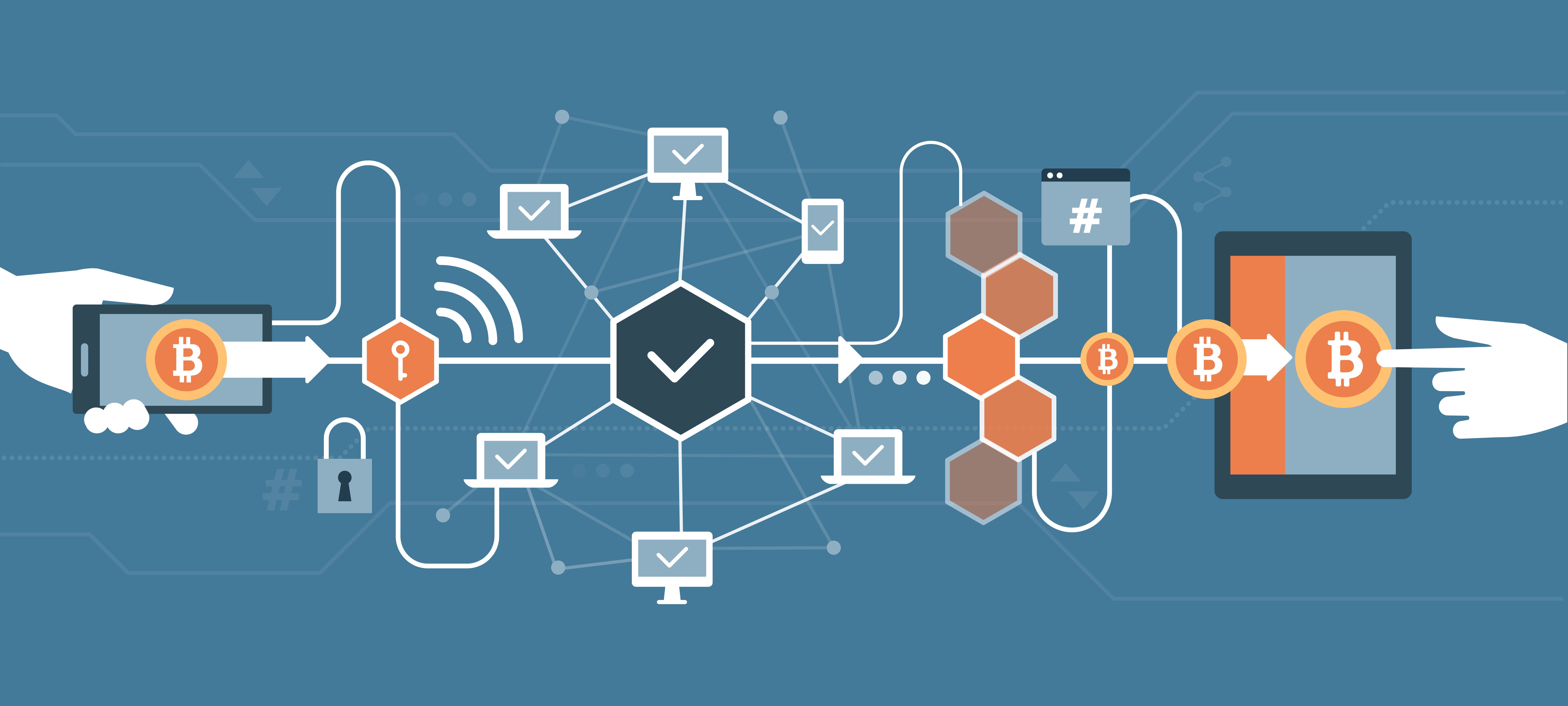
At its core, a blockchain is a distributed, immutable ledger that records and verifies transactions in a secure and transparent manner. Imagine a digital record-keeping system replicated across numerous computers (nodes) in a network. Each block in the chain contains a batch of verified transactions, linked cryptographically to the previous block, creating an unbroken chain of records. This interconnectedness ensures the integrity and security of the data, making it extremely difficult to alter or delete information once it’s been added to the chain.
Several key features distinguish blockchain technology:
-
Decentralization: Unlike traditional centralized databases controlled by a single entity, blockchain networks are decentralized, meaning no single entity controls the data. This distributed nature enhances security and resilience, as the system is not vulnerable to single points of failure.
-
Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring data integrity and transparency. This immutability is achieved through cryptographic hashing, where each block is linked to the previous block through a unique cryptographic hash. Any attempt to alter a previous block would change its hash, breaking the chain and making the alteration immediately apparent.
-
Transparency: While the identities of participants may be pseudonymous (using cryptographic keys instead of names), all transactions are publicly viewable on the blockchain, fostering trust and accountability. However, the level of transparency can be adjusted depending on the specific blockchain implementation, with some offering varying degrees of privacy.

Security: The cryptographic hashing and distributed nature of blockchain make it highly secure. The sheer number of nodes in the network makes it computationally infeasible to compromise the entire system. Moreover, consensus mechanisms ensure that only valid transactions are added to the blockchain.
Consensus Mechanisms: The Heartbeat of Blockchain
To ensure the integrity of the blockchain, a consensus mechanism is employed to validate transactions and add new blocks to the chain. Various consensus mechanisms exist, each with its own strengths and weaknesses:

-
Proof-of-Work (PoW): Used in Bitcoin, PoW requires miners to solve complex computational puzzles to validate transactions and add new blocks. The first miner to solve the puzzle gets to add the block and receives a reward in cryptocurrency. While secure, PoW is energy-intensive.
-
Proof-of-Stake (PoS): PoS is a more energy-efficient alternative to PoW. In PoS, validators are selected based on the amount of cryptocurrency they stake. The more cryptocurrency a validator stakes, the higher the probability of being selected to validate transactions and add new blocks.
-
Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS): DPoS allows token holders to vote for delegates who will validate transactions and add blocks to the chain. This mechanism reduces the energy consumption and improves transaction speed compared to PoW.
-
Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT): PBFT is a deterministic consensus mechanism that ensures agreement among nodes in the presence of Byzantine failures (malicious nodes). It’s suitable for smaller, permissioned blockchain networks.
Beyond Cryptocurrency: Diverse Applications of Blockchain
While blockchain’s initial association with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum is undeniable, its potential extends far beyond the realm of digital currencies. The technology’s transformative power is being harnessed across a wide range of industries:
-
Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can enhance supply chain transparency and traceability by tracking goods from origin to consumer, combating counterfeiting and improving efficiency.
-
Healthcare: Securely storing and sharing patient medical records on a blockchain can improve data privacy and interoperability.
-
Finance: Blockchain is revolutionizing financial services, enabling faster and cheaper cross-border payments, streamlining KYC/AML processes, and facilitating the development of decentralized finance (DeFi) applications.
-
Voting Systems: Blockchain-based voting systems can enhance the security and transparency of elections, reducing the risk of fraud and manipulation.
-
Digital Identity: Blockchain can provide individuals with secure and verifiable digital identities, simplifying online interactions and reducing identity theft.
-
Intellectual Property Protection: Blockchain can help protect intellectual property rights by providing a tamper-proof record of ownership and creation dates.
-
Real Estate: Blockchain can streamline real estate transactions, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
Advantages of Blockchain Technology
The adoption of blockchain technology offers several compelling advantages:
-
Increased Security: The decentralized and immutable nature of blockchain makes it highly secure, reducing the risk of data breaches and fraud.
-
Enhanced Transparency: The public nature of blockchain transactions fosters trust and accountability.
-
Improved Efficiency: Blockchain can automate processes, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
-
Greater Data Integrity: The immutability of blockchain ensures data integrity, making it difficult to alter or delete information.
-
Increased Trust: The decentralized and transparent nature of blockchain builds trust among participants.
Challenges and Limitations of Blockchain
Despite its potential, blockchain technology faces several challenges:
-
Scalability: Some blockchain networks struggle to handle a large number of transactions, limiting their scalability.
-
Regulation: The regulatory landscape surrounding blockchain technology is still evolving, creating uncertainty for businesses.
-
Energy Consumption: Proof-of-work consensus mechanisms can be energy-intensive, raising environmental concerns.
-
Complexity: The technical complexity of blockchain can make it difficult for some businesses to implement and utilize.
-
Interoperability: Different blockchain networks often lack interoperability, hindering seamless data exchange.
The Future of Blockchain Technology
The future of blockchain technology is bright, with ongoing research and development focused on addressing existing challenges and expanding its applications. We can expect to see further advancements in scalability, interoperability, and regulatory clarity. The convergence of blockchain with other emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT), will unlock even greater potential.
Blockchain is not a panacea, but it is a powerful technology with the potential to transform industries and reshape our digital world. As the technology matures and its applications broaden, we can anticipate a future where blockchain plays an increasingly crucial role in various aspects of our lives. The journey has just begun, and the possibilities are limitless.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Blockchain: The Revolutionary Technology Reshaping Industries. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!